STAFFING PROCESS/ HIRING PROCESS
Staffing is a management function that focuses on hiring, training, and retaining talent for organizational roles. The staffing function encompasses activities like recruiting, selecting, promoting, and transferring the right person to fill a vacant position in the organization. To understand more about how staffing works, it is essential to know about the key components of staffing. Before we delve into the components of staffing process, let us look at what staffing essentially is.
What is Staffing? (Definition and meaning)
Staffing is the process of identifying, screening, and hiring the right individuals to fill open positions in an organization. Staffing is crucial function of management, and it involves matching candidates with the specific skills and knowledge required for roles, ultimately helping organizations create an effective and productive workforce.
Why are the Components of Staffing Important?
The components of staffing (manpower planning, recruitment and selection, placement and training, development, promotion, and appraisal) are important as it ensures that an organization has the right people in the right roles, leading to better productivity. Components of strategic staffing work together to build a skilled workforce.
1. Assessment of manpower needs
One of the main components of staffing, manpower planning helps determining the specific manpower needs of the business, which usually varies from season to season and is likely to change based on evolving economic conditions.
2. Placement and hiring
Detailed job descriptions are churned out to attract the best-qualified candidates. It ensures that applicants understand the requirements and responsibilities of the advertised open job positions and what the interviewers are looking for during the screening process.
3. Bringing employees up to speed with training and company culture
Effective staffing involves a full-spectrum introduction to a business’s corporate culture, including skills training as well as educating the employees regarding a company’s policies and procedures. Adding fresh staff members to an existing employee pool should include peer training and mentoring to maintain and bolster a company’s productivity.
4. Workforce Development
Post the hiring and training of an employee, they are paired with the right employees with the proper job responsibilities. This is achieved by assessing individual skills, talents, and experience levels. Employees, by now, have a full understanding of their duties. Ongoing training and development for new employees ensures efficient workplace productivity.
5. Boost Business Operations
Employees are provided with professional training and development opportunities. Job mentoring and job shadowing can encourage employees to learn more about the industry increasing their ability to contribute to the productivity and longevity of the organization.
6. Maintaining Workforce Longevity
Another major importance of one of the components of staffing process is that it can help businesses retain employees for a longer period, facilitating the development and nurturing a skilled, seasoned workforce. Employee incentive programs are a great way to boost employee morale and plays a key role in supporting long-term employment.
What are the 10 Key Components of Staffing?
Staffing function in an organization consists of several components. Here are 8 crucial components of staffing that you must know-
1. Manpower Planning
As the name suggests this is the phase where the organization and the staffing partner map out the exact workforce needs of the organization. It involves the analysis of current workforce and predicts the future manpower requirements to ensure that organization goals are met.
2. Recruitment
The recruitment process involves several tasks including identifying and sourcing candidates by using various sourcing channels like relevant job boards, networking, leveraging social media to get in touch with passive and active candidates. This helps match individuals with specific skills with the right roles to ensure better productivity.
3. Selection
Post the sourcing of candidates, the selection process begins wherein resumes of candidates are scrutinised and they are assessed based on their skills and experience, post which interviews are conducted to ensure the right candidates are selected.
4. Placement
The selected candidates are to be placed in the right roles to ensure the best use of their skills as well as lead to greater productivity of the organisation.
5. Orientation
Once the job role of a candidate is decided and the candidate is made aware of the duties and responsibilities to be carried out, an orientation program is conducted. The program helps the new employee get acquainted with the company culture, policies, and procedures.
6. Training and Development
Training is an essential part of the staffing process as it helps keep the employees updated on the way of work in an organisation. With the advances in technology and newer technologies come to life, companies must train employees help them understand the modern technology and make the best use of it.
Development refers to the opportunity of growth of the employees in the organisation. The organisation must provide ample opportunities for the development of the employees, without which the employees may become frustrated.
7. Promotion
Once the employee is settled in and has way past his probation period and is consistently performing well, around the one-year mark, in most cases, they are given a raise in salary or a better designation or both.
8. Transfer
Transfer is the process of shifting of an employee from one position to another in the organisation without any monetary benefit, or any increase in the responsibilities. This function needs to be evaluated from time to time.
9. Appraisal
Similar to the promotion stage, employees upon successful completion of their tasks over a period of time, based on several other factors like company budget, as well as how well the employee performed, they get an appraisal.
10. Determination of Remuneration
The remuneration of an employee is especially important for sustenance. It is regarded as one of the difficult functions to perform as there exists no tools which can accurately determine wages.
Staffing is more than just filling vacancies; it is a strategic process that ensures the right people are placed in the right roles at the right time. By focusing on its key components that include workforce planning, talent acquisition, selection, onboarding, training, and retention, organizations can build a strong foundation for long-term success.
A well-structured staffing strategy not only improves productivity and morale but also aligns talent management with business goals. In today’s competitive landscape, companies that invest in thoughtful, data-driven staffing practices will be better positioned to attract top talent, reduce turnover, and drive sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main components of staffing?
The main components of staffing include manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, training and development, performance appraisal, and compensation. These components work together to ensure that an organization has the right people in the right roles at the right time, capable of effectively achieving its goals.
2. What is the difference between staffing and recruitment?
Staffing is done to satisfy a temporary or contractual need which can transform into a permanent role. In recruitment, the goal is to hire for a permanent position. These days many companies are opting for contract staffing solutions as they prefer flexibility.
3. Why is workforce planning important in staffing?
Workforce planning is very important in staffing because it helps meet current client needs, retain employees for longer, enables better training initiatives, boosts employee engagement, and eventually, builds a better reputation for the company.
4. What tools help manage staffing effectively?
Several tools can help manage staffing effectively, including Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), workforce management software, and performance management tools. These tools streamline the hiring process, manage employee records, and facilitate performance evaluations, leading to better workforce planning and decision-making.
5. What are the steps in the staffing process?
The staffing process involves several steps which include- determining manpower needs, recruitment of candidates, selection of candidates, orientation and placement, training and development and evaluation of performance, manager promotions, transfers and finally addressing of remunerations.
STAFFING
BY JONES MUNA.
As we have seen so far, the role of the nurse manager is a demanding and
involving one. Allocating human resources is one of the many responsibilities
and a challenge to the manager. This lecture will introduce you to the managerial
function of staffing including staffing process, scheduling and factors
affecting staffing.
STAFFING PROCESS
The process of staffing
involves: Recruitment, Selection, Induction and Scheduling
Let us examine
the meaning of each of
the above terms:
i.
Recruitment
This is the first part of the process and it involves
filling a vacancy.
It is the drafting or revision of the job specification for the vacant
position, outlining the qualifications, experience, skills and the
responsibilities involved.
The vacancy is then advertised to source suitable candidates. The sources could be internal, that is,
from within the organization or external.
ii.
Selection
Selecting is the next stage
which involves matching the requirements
of the job with the attributes of the candidate. The process includes
assessing the candidate by various means eg. Interviewing and screening. The
purpose of this is to obtain information. Selection testing including
achievement, aptitude, intelligence and personality may also be used. These are followed by offer of employment
iii.
Induction
This is the process of receiving employees when they begin work,
introducing them to the organization and to their colleagues and informing them
of the activities, and the culture of the organization. This may be regarded as the orientation or beginning of training.
iv.
Scheduling(Duty Roster)
After induction is given, the employee is assigned the tasks to be
performed. The schedules for work and time off should meet organizational goals
with fairness and equality among personnel. A
schedule should adhere to following:
•
Policies, standards and practices of the organization on the use of professional and
paraprofessional personnel (Supportive staff).
•
Appropriate ratio or balance between professional and supportive staff.
This is in order to deliver continuity of services nursing care.
•
Approved budget. The manager should consider the financial resources
within the
organization.
•
Consideration of vacations and consideration of allowance of adjustment
in case of illness, emergencies or
changes in patient care needs.
It is important
to inform staff members of their work
schedules at least 1-3 weeks in advance. This
allows time for planning.
Factors Affecting Staffing
Various factors affect nursing staffing or determinations. The manager
needs to be sensitive about these in order to achieve the objectives of
staffing. One is the need to provide hospital and nursing services 24 hours a
day.
-
Patient factors e.g Unpredictability of the patient
census, variety of patient conditions, patient population, and care needs.
-
Staff factors including, experiences and expectations
of the organization, job descriptions, education level and personnel
requirements.
-
Health care
organization factors e.g. policies and procedures, resources available and number of beds per unit
-
Since each setting is unique, there is no guide that
can stipulate the correct number of personnel needed to provide quality care
but systems have been developed for guidance eg. patient classification system
which is a method of grouping patients according to the amount and complexity
of their nursing care requirements. In
this case patients are grouped according to the nursing time, effort and
ability required to provide care.
Types of Schedules (Rosters)
The two types of schedules
frequently used are centralized and decentralized.
i.
Centralized Schedules
These are
completed by matron (Chief Nurse) or designate who develops a master plan for
nursing personnel in the hospital or health facility.
The advantages for these are that they:-
-
Provide overall picture
of the staffing situation.
-
Enable easier adjustments in case of illness or
emergencies or changes in patient care needs among the departments.
-
Eliminate personnel biases or prejudices
-
Reduce frequent requests
by staff for special privileges.
Some of the disadvantages include:
-
Denies manager the right to make scheduling decision.
-
The person making them has limited knowledge of
workers abilities, interests or needs and also limited knowledge of nursing
needs in separate departments.
ii.
Decentralized Schedules
These schedules have a more personal
approach than the previous ones.
The middle and lower level of management
determine scheduling e.g ward in
charges.
The advantages for this are that the Nurse Manager is accountable.
Secondly, the scheduling based on knowledge of personnel and patient needs. There is greater control of activities
such that the manager can rearrange schedules as needed.
There are also some disadvantages
of this type of schedule.
These are
-
Increased number of requests for special privileges.
- Many result
in insufficient numbers of qualified personal to meet unforeseen needs.
-
May be time consuming.
-
In summary, staffing is the use of: Recruitment of staff
(Nurses), interviewing and screening of nurses, employing all categories of
nursing personnel, assigning staff to clinical areas and to specific work
hours, preparing time schedules for the various groups of personnel while
adjusting to meet needs of patients and absenteeism.
STAFFING
Staffing is a very important part of running a business or an organisation. It is referred to as the process of obtaining and hiring of manpower for the various business requirements. Staffing is regarded as an essential managerial function.
An enterprise is unable to run its operations without the help of human resources. Therefore, human resources play an important role in the functioning of an organisation.
Staffing process consists of the following steps:
1. Manpower Planning
2. Recruitment
3. Selection
4. Placement
5. Training
6. Development
7. Promotion
8. Transfer
9. Appraisal
10. Determination of Remuneration
We will be discussing all these steps in detail in the following lines.
Manpower Planning: Manpower planning is the quantitative and qualitative measurement of the manpower that is required in an organisation. It involves evaluation and creation of the manpower inventory and also to develop the necessary talents among the employees that are selected for obtaining promotion.
Recruitment: Recruitment is the process of finding the potential employees of an organisation and persuading them to apply for the available positions in the organisation. If the recruitment process is followed scientifically, then it will result in better wages, high morale and higher productivity among the employees.
Selection: Selection is the process of shortlisting of potential candidates and eliminating the candidates that are not suitable for the positions available in the organisation. The purpose of selection is to hire the right candidate for the right position, which will lead to efficient running of operations for the organisation.
Placement: Placement refers to the process of introducing an employee to the job for which he was hired in the organisation. The employee will be provided with a basic orientation about the company and its work areas.
Training: Training is the process of providing the newly recruited employees an idea about the type of work that they are going to do and how to do that. This falls under the training department.
Training is an essential part of hiring as it helps keep the employees updated on the way of work in an organisation. Also due to advances in technology, newer technologies will evolve, that makes it necessary for employees to be updated with the latest development.
Development: Development refers to the opportunity of growth of the employees in the organisation. The organisation must provide ample opportunities for the development of the employees, without which the employees may become frustrated.
Promotion: Promotion is referred to as the process of giving the employees a raise in salary, designation or both. The raise in designation is associated with a raise in wages or bonus or incentives. There can be some instances where the change in designation does not result in increase in pay.
Transfer: Transfer is the process of shifting of an employee from one position to another in the organisation without any monetary benefit, or any increase in the responsibilities. This function needs to be evaluated from time to time.
Appraisal: Appraisal is the process of checking the progress of the work done by the subordinates. It also studies human behavior and also the attitude and aptitude of the employee towards performing the job.
Determination of Remuneration : The remuneration of an employee is very important for sustenance. It is regarded as one of the difficult functions to perform as there exists no tools which can accurately determine wages.
Benefits of Staffing Process
Following are some of the benefits of the staffing processes:
1. It helps in getting the right person for the right position in an organization.
2. It helps in improving the organisational productivity as proper selection process, increases the quality of employees, which coupled with training results in better productivity.
3. It keeps employee morale high and also provides them job satisfaction.
4. It helps in maintaining a harmonious working environment inside the organisation.
This concludes the topic of Staffing process, which is an important topic of Business Studies for Commerce students. For more such interesting articles, stay tuned to.
STAFFING
Introduction
An effective staffing process is the backbone of any successful organization. It ensures that people with the right skills are in the right positions at the right time. A well-designed staffing process helps attract and retain top talent and aligns the workforce with the organization’s strategic goals. In today’s competitive business landscape, having a robust staffing process is more critical than ever.
This comprehensive blog post will explore the world of staffing, its definition, the eight essential steps, best practices, and specific considerations for IT staffing. Whether you are an HR professional, a hiring manager, or a business owner, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical tips to optimize your staffing process and build a high-performing workforce.
Throughout this blog, we will cover the key aspects of the staffing process, from workforce planning and job analysis recruitment, selection, and onboarding. We will also discuss the unique challenges and strategies specific to IT staffing, recognizing the crucial role of technology professionals in driving business success. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of how to design and implement an effective staffing process that aligns with your organizational objectives
What is the Staffing Process?
The staffing process is a systematic approach to finding, selecting, and onboarding the most qualified candidates for an organization. It encompasses a series of steps designed to ensure that the right people are hired for the right positions at the right time and in the right quantities. The staffing process is a critical component of human resources management, as it directly impacts an organization’s ability to achieve its goals and maintain a competitive edge.
An effective staffing process aims to:
- Identify and assess the organization’s current and future workforce needs
- Attract a diverse pool of qualified candidates
- Select the most suitable candidates based on job requirements and organizational fit
- Onboard and train new hires to ensure their success in their roles
- Continuously evaluate and improve the staffing process to adapt to changing business needs
The 8 Steps of the Staffing Process
The staffing process has eight essential steps, each crucial to building a high-performing workforce. Let’s explore each step in detail.
Step 1: Workforce Planning
Workforce planning is the foundation of the staffing process. It involves assessing the organization’s current workforce, identifying future staffing needs, and developing strategies to bridge gaps. This step requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s strategic goals, industry trends, and anticipated changes in the business environment.
Key activities workforce planning include:
- Analyzing the current workforce composition and skills inventory
- Forecasting future staffing requirements based on business objectives and growth projections
- Identifying potential skill gaps and talent shortages
- Developing strategies to address staffing needs, such as recruitment, training, or succession planning
Step 2: Job Analysis and Design
Once the workforce planning is complete, the next step is to analyze and design the job roles that need to be filled. Job analysis involves gathering information about a job’s duties, responsibilities, and requirements. This information is used to create job descriptions and specifications, the foundation for recruitment and selection.
Key activities in job analysis and design include:
- Conducting job analysis through interviews, questionnaires, and observations
- Defining the essential functions, tasks, and responsibilities of each job
- Identifying the knowledge, skills, and abilities required for successful job performance
- Creating detailed job descriptions and specifications
Step 3: Recruitment
Recruitment is the process of attracting a pool of qualified candidates for the job openings identified in the workforce planning stage. It involves creating job postings, advertising open positions, and actively seeking out potential candidates through various channels.
Key activities in recruitment include:
- Developing a recruitment strategy based on the job requirements and target candidate profile
- Creating compelling job postings and advertisements
- Leveraging various recruitment channels, such as job boards, social media, employee referrals, and recruitment agencies
- Building a strong employer brand to attract top talent
Step 4: Selection
The selection step involves evaluating the pool of candidates generated during the recruitment phase and choosing the most suitable individuals for the job. This step typically includes several stages: resume screening, interviews, assessments, and reference checks.
Key activities in selection include:
- Screening resumes and applications to identify candidates who meet the minimum job requirements
- Conducting interviews to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and fit with the organization’s culture
- Administering job-related assessments or tests to evaluate candidates’ abilities and potential
- Conducting reference checks and background investigations to verify candidates’ information and suitability
Step 5: Hiring
Once the most suitable candidate is identified, the hiring step involves making a job offer and completing the necessary paperwork. This step also includes negotiating compensation and benefits and meeting all legal and regulatory requirements.
Key activities in hiring include:
- Extending a job offer to the selected candidate
- Negotiating compensation, benefits, and other terms of employment
- Conducting pre-employment screenings, such as drug tests or medical examinations, if required
- Completing the necessary paperwork, such as employment contracts and tax forms
Step 6: Onboarding and Training
Onboarding and training are critical in helping new hires integrate into the organization and become productive team members. Onboarding involves orienting new employees to the company’s culture, policies, and procedures, while training provides them with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their jobs effectively.
Key activities in onboarding and training include:
- Develop a comprehensive onboarding program that covers the company’s history, mission, values, and policies
- Assigning mentors or buddies to help new hires navigate the organization and build relationships
- Providing job-specific training to ensure new employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed
- Setting clear expectations and goals for new hires’ performance and development
Step 7: Performance Management
Performance management is an ongoing process that involves setting goals, providing feedback, and evaluating employees’ contributions to the organization. This step ensures employees meet expectations and continuously improve their skills and performance.
Key activities in performance management include:
- Setting clear, measurable goals and objectives for each employee
- Providing regular feedback and coaching to help employees improve their performance
- Conducting periodic performance evaluations to assess employees’ progress and identify areas for development
- Recognizing and rewarding high-performing employees to boost motivation and retention
Step 8: Retention and Turnover
The final step in the staffing process is managing retention and turnover. While some turnover is inevitable, high turnover rates can be costly and disruptive to the organization. Effective retention strategies help keep top talent engaged and committed to the organization.
Key activities in retention and turnover management include:
- Identifying the root causes of turnover through exit interviews and surveys
- Developing retention strategies, such as competitive compensation, career development opportunities, and work-life balance initiatives
- Creating a positive work environment that fosters engagement, collaboration, and recognition
- Continuously monitoring and analyzing turnover rates to identify trends and areas for improvement
Recruitment and Selection in the Staffing Process
Recruitment and selection are two critical steps in the staffing process that directly impact the quality of new hires. Let’s examine these steps and the strategies involved.
Recruitment Strategies
Effective recruitment strategies are essential for attracting a diverse pool of qualified candidates. Some common recruitment strategies include:
- Employee referrals: Encouraging current employees to refer candidates from their professional networks
- Job boards and online platforms: Posting job openings on popular job search websites and industry-specific platforms
- Social media recruiting: Leveraging social media platforms, such as LinkedIn, to reach out to potential candidates promote job openings
- Campus recruiting: Partnering with universities and colleges to attract fresh talent
- Recruitment events: Participating in job fairs, industry conferences, and other events to meet potential candidates in person
Selection Methods
Once a pool of candidates has been generated through recruitment efforts, the next step is to evaluate and select the most suitable individuals for the job. Some common selection methods include:
- Resume screening: Reviewing resumes and applications to identify candidates who meet the minimum job requirements
- Interviews: Conducting structured or unstructured interviews to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and fit with the organization’s culture
- Assessments and tests: Administering job-related assessments, such as personality tests, cognitive ability tests, or technical skill tests, to evaluate candidates’ potential
- Reference checks: Contacting candidates’ references to verify their work history, skills, and character
- Background checks: Conducting background investigations, such as criminal record checks or credit checks, to ensure candidates’ suitability for the position
IT Staffing Process
The IT staffing process presents unique challenges and considerations due to the rapidly evolving nature of technology and the high demand for skilled IT professionals.
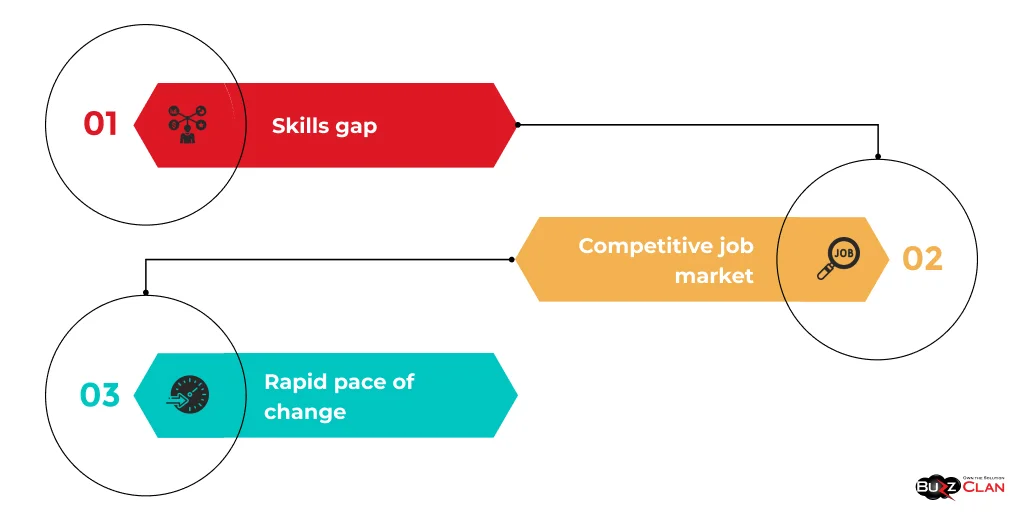
Unique Challenges
Some of the unique challenges faced in the IT staffing process include:
- Skills gap: The technology landscape constantly changing, making it difficult to find candidates with the latest skills and expertise
- Competitive job market: High demand for IT professionals leads to intense competition for top talent
- Rapid pace of change: IT roles and requirements can change quickly, requiring a flexible and adaptable staffing process
Specialized Skills
IT staffing often requires identifying and recruiting candidates with specialized skills, such as:
- Programming languages and frameworks
- and infrastructure
- Cybersecurity and data protection
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- and agile methodologies
IT Recruitment Strategies
To overcome these challenges and attract top IT talent, organizations can employ specific recruitment strategies, such as:
- Emphasizing the organization’s technology stack and innovative projects in job postings
- Partnering with technology schools and boot camps to identify promising candidates
- Offering competitive compensation packages and benefits, such as flexible work arrangements or professional development opportunities
- Building a strong employer brand that showcases the organization’s technology culture and values
Best Practices for an Effective Staffing Process
Organizations should follow best practices that promote fairness, efficiency, and continuous improvement to ensure a successful staffing process.
Diversity and Inclusion
Promoting in staffing is a legal and ethical imperative and a business advantage. Diverse teams bring a wider range of perspectives and experiences, leading to better decision-making and innovation.
Best practices for promoting diversity and inclusion in staffing include:
- Using inclusive language in job postings and eliminating bias in job requirements
- Conducting blind resume screening to minimize unconscious bias
- Providing diversity and inclusion training for hiring managers and interviewers
- Setting diversity goals and regularly monitoring and reporting on progress
Continuous Improvement
The staffing process should be continuously evaluated and improved to adapt to changing business needs and candidate expectations. Regular feedback from hiring managers, new hires, and other stakeholders can provide valuable insights into areas for improvement.
Best practices for continuous improvement in staffing include:
- Establishing metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the staffing process
- Conducting surveys and interviews to gather feedback from candidates and new hires
- Regularly reviewing and updating job descriptions and requirements to ensure they remain relevant
- Investing in technology and tools to streamline and automate parts of the staffing process
Technology and Tools
Technology is increasingly important in staffing, from applicant tracking systems (ATS) video interviewing platforms. These tools can help organizations manage large volumes of candidates, reduce time-to-hire, and improve the overall candidate experience.
Best practices for leveraging technology in staffing include:
- Implementing an ATS to streamline candidate management and communication
- Using video interviewing platforms to screen candidates remotely and efficiently
- Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to automate resume screening and candidate matching
- Investing in to gain insights into the staffing process and make data-driven decisions
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The staffing process is subject to various legal and ethical considerations, such as equal employment opportunity laws, data privacy regulations, and fair hiring practices. Organizations must ensure compliance with these requirements to avoid legal risks and maintain a positive reputation.
Best practices for legal and ethical staffing include:
- Ensuring that all hiring practices comply with equal employment opportunity laws and regulations
- Protecting candidate and employee data by data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA
- Providing training on legal and ethical hiring practices for all individuals involved in the staffing process
- Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance and identify potential risks
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the key aspects of the staffing process, including recruitment and selection strategies, best practices for IT staffing, and the importance of diversity, continuous improvement, technology, and legal compliance. Organizations can gain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly changing business landscape by implementing these best practices and continuously evaluating and improving their staffing process.
STAFFING PROCESS.
What Are the Seven Steps in the Staffing Process?
Staffing is a key function in human resource management that ensures an organization has suitable employees in the right roles so its objectives can be achieved efficiently. At its core, staffing involves not just hiring, but also planning, training, and developing the workforce. This process is essential for all businesses and organizations, regardless of size or industry.
Definition of Staffing
Staffing is the process of filling organizational roles with competent and qualified individuals. It starts with estimating workforce needs and ends with placing and developing employees within the business. An effective staffing process ensures every role in an organization is occupied by the best-suited person. This supports both daily operations and long-term organizational goals.
Steps in the Staffing Process
The staffing process involves several critical steps. Each step is designed to gradually build up a productive and satisfied workforce. Below is an overview of each step:
Step Description Manpower Planning Identify the number and type of employees required to meet business goals. Assess current workforce, examine future needs, and determine skills required for each position. Recruitment Attract potential candidates to apply for job openings. Jobs are advertised through different channels to reach eligible applicants. Selection Screen applicants and select the best fit for the role. This involves interviews, tests, and background checks. Orientation and Placement Introduce new employees to the organization and assign them to their respective jobs for smooth integration. Training and Development Provide learning opportunities to enhance employees’ skills and keep them updated for current and future roles. Remuneration Offer fair compensation for the work performed, based on role complexity, responsibilities, and performance. Performance Evaluation Assess how employees perform in their roles. This includes regular appraisals and feedback to help identify strengths and areas of improvement. Promotion and Transfer Move employees to higher positions (promotion) or across departments or locations (transfer) for growth and organizational development. Types of Staffing Process
Staffing can be handled in several ways depending on needs:
- Internal Recruitment: Filling roles with current employees through promotions, transfers, or internal postings.
- External Recruitment: Attracting outside candidates via job ads, recruitment agencies, or campus placements.
- Short-Term Staffing: Hiring for seasonal or project-based requirements.
- Contractual Staffing: Engaging employees for a fixed period.
- Project-Based Staffing: Recruiting teams for specific projects with defined timelines.
- Outsourced Staffing: Utilizing agencies or firms to manage hiring and workforce supply.
Difference Between Recruitment and Selection
Basis Recruitment Selection Objective Attract as many qualified applicants as possible Identify and choose the best candidate for the job Nature Positive process — increases applicant pool Negative (elimination) process — filters out unsuitable Sequence Precedes selection Follows recruitment Result List of prospective candidates Appointment of selected candidate Importance and Benefits of Effective Staffing
- Ensures each position is matched with qualified employees.
- Improves efficiency and productivity throughout the organization.
- Enhances employee morale and job satisfaction, reducing turnover.
- Provides opportunities for growth through training, promotion, and skill development.
- Supports harmonious work environments and teamwork.
Application Example
Suppose a company wants to launch a new product. The manager starts with manpower planning to determine how many sales staff are needed. After recruitment and selection, the hired employees are oriented and trained. Their performance is then regularly appraised, and outstanding staff may get promoted.
Step-by-Step Approach to Staffing Problems
- Identify workforce needs and define job roles clearly.
- Conduct recruitment to reach eligible and interested candidates.
- Screen applicants through selection tests or interviews.
- Orient and assign selected candidates to departments and teams.
- Implement training to meet job requirements and fill skill gaps.
- Set up fair compensation and recognition systems.
- Continuously review employee performance and provide constructive feedback.
Key Principles and Concepts
- Staffing is a continuous and dynamic process, not a one-time event.
- Right people in the right roles drive organizational success.
- Balanced focus on recruitment, selection, training, and appraisal is essential.
- Both internal and external sources should be considered for talent.
Vedantu Resources and Next Steps
- Review sample staffing questions and solve related problems using Vedantu's online study materials.
- Practice MCQs and case studies for better understanding of recruitment and selection.
- Explore practical examples and role-play scenarios to strengthen application skills.
Mastering the staffing process prepares students not only for exams but also for real-world HR situations and future leadership roles. With the right understanding, students can efficiently approach staffing-related questions and contribute to building effective teams in any organizational setup.





.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment