MENTAL HEALTH REVISION 1 OUT 4
SECTION
A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (50 MARKS)
Encircle
the most appropriate answer ONE (1) MARK EACH.
1. Mental
disorders are defined by
a) Confirmation
of how the individual acts
b) Behavior
and what the individual thinks
c) How
the person feels, acts and perceives things
d) Talking
a lot
2. The
term Psych from psychiatry in Greek means:-
a) Disease
b) Confusion
c) Mental
processes
d) Healing
3. Psychiatry
nursing is a speciality concerned with
a) People’s
health
b) Application
of health principles in nursing care
c) Application
of psychiatric principles in nursing care
d) Patients
with mental problems
4. A
mental disorder manifested with severe impaired thinking, emotions and behavior
is called
a) Schizophrenia
b) Hallucinations
c) Mania
d) Hypomania
5. The
biggest mental health hospital, Chainama Hills was opened in
a) 1962
b) 1960
c) 1964
d) 1965
6. Training
of enrolled psychiatric nurse at Chainama Hills Hospital started in
a) 1967
b) 1966
c) 1968
d) 1980
7. Psychiatric
patients at times believe that there thoughts are known by other people. This
is called
a) Thought
broadcasting
b) Thought
insertion
c) Hallucinations
d) Thought
withdraw
8. A
mental disorder characterized by persecutory delusions and inflicting harm is
known as
a) Simple
schizophrenia
b) Paranoid
schizophrerenia
c) Catatonic
schizophrenia
d) Hebephrenia
schizophrenia
9. A
mood disorder is also referred to as
a) affective
disorder
b) Irritable
disorder
c) Cognitive
disorder
d) Mania
10. The
following are causes of mood disorders EXCEPT
a) Hereditary
factors
b) Emotional
stability
c) Stressful
life events
d) Illnesses
11. The
following are examples of obsessive behavior except
a) Fear
of losing things
b) Fear
of contamination
c) Fear
of losing a spouse
d) Severe
anxiety
12. Panic
disorder is common in
a) Women
b) Children
c) Men
d) Females
and men
13. Cognitive
behavioral therapy is indicated in
a) anxiety
disorder
b) Panic
disorder
c) Compulsive
disorder
d) Mood
disorder
14. Anxiety
which results from traumatic experience is called
a) Stress
disorder
b) Pre
stress disorder
c) Post
traumatic disorder
d) Traumatic
disorder
15. Persistent
and emotional fear of any specific object or situation is called
a) Stress
b) Phobia
c) Phobic
stress
d) Emotional
upset
16. Fear
of a situation in which an individual may be exposed to scrutiny by others is
known as
a) Agoraphobia
b) Social
phobia
c) Photophobia
d) Phobia
17. The
common type of phobia among women is
a) Social
phobia
b) Specific
phobia
c) Photophobia
d) Agoraphobia
18. Which
of the following is not commonly associated with a psychiatric disorder
a) Anxiety
b) Personality
changes
c) Agitation
d) Good
memory
19. A
relationship in which the client is helped to make a decision is called
a) Teaching
b) Communication
c) Counselling
d) Friendship
20. Treatment of a mental patient through psychological
method is also known as
a) Psychotherapy
b) Phototherapy
c) Chemotherapy
d) Pharmacotherapy
21. The
acronym that best demonstrates and summarizes behavior during counselling
sessions is known as…………
a. Counselling
therapy
b. Behavior
modification
c. Soler
d. Counselling
skills
22. The
inability to recognize objects and people is known as…..
a. Alogia
b. Apraxia
c. Agnosia
d. Aphasia
23. The
most common cause of dementia is
a. HIV/AIDS
b. Cerebral
vascular accident
c. Stroke
d. Alzheimer’s
disease
24. The
type of Schizophrenia where a person has symptoms of both Schizophrenia and a
major mood disorder such as depression is called:-
a) Paranoid
Schizophrenia
b) Catatonic
Schizophrenia
c) Schizoaffective
disorder
d) Simple
Schizophrenia
25. Anxiety
is caused by….
a. Objective
threat
b. Subjective
perceived threat
c. Hostility
turned to self
d. Masked
depression
26. Which
drug is mostlyq indicated in anxiety
a. Modicate
b. Lithium
c. Prozac
d. Valium
27. Fragmented
thinking means……………….
a) Beating
about the bush
b) Having
disjointed ideas
c) Ideas
coming into your mind frequently
d) Repeating
what the interviewer says
28. The
only institution in Zambia ,which is used to confine people who have committed
homicide or grievous bodily harm to
others, as a result of being insane is;.
a) Chainama
North
b) Chainama
west
c) Chainama
South
d) Chainama
East
29. Which
one of the following drugs is a tricyclic anti-depressant
a. Iripiprazole
b. Imipramine
c. Trifluoperazine
d. Diazepam
30. ……..
is an anti-psychotic drug belonging to the family of typical antipsychotics
a. Sertraline
b. Trifluoperazine
c. Imipramine
d. Iripiprazole
31. Which
one of these best describes self-awareness skills
a. It
is about teaching the patient step by step way of changing bad behavior and
learn good behaviour.
b. It’s
about inspecting oneself inwardly
c. Its
about training patient to express themselves in an appropriate way
d. Its
about helping patient change abnormal behavior
32. An
affective disorder which presents with elation of mood and increased
psychomotor activities is called………………
a. MDD
b. Neurosis
c. Mania
d. Hysteria
33. Thought
broadcasting is described as……..
a. Thoughts
made aware to oneself
b. Belief
that thoughts are being taken away from oneself.
c. A
belief that ones thoughts are being shared by others
d. Misinterpretation
of external stimuli
34. A
form of hostile aggression that does damage to another's peer relationships, as
in social exclusion or rumor spreading
a. Hostile
aggression
b. Relational
aggression
c. Instrumental
aggression
d. Fear
induced aggression
35. ........are
internal debates in which arguments for and against even the simplest every day actions are reviewed endlessly.
a. Obsessional phobias
b.
Obsessional doubts
c. Obsessional rumination
d.
Obsessional rituals
36. Echopraxia is defined as…..
a. Purposeless imitation of others
b. Absence of emotional expression in person
c. Difficulties in finding the right word
d. False perception or response to stimulus
37. The outward expression of the immediate experience
of emotions at a given time is called..
a. Mood
b. Illusion
c. Behaviour
d. Affect
38. ……
is the knowledge and skills people need to have to live in the community.
a. Assertive
skills
b. Counselling
skill
c. Reacreation
skills
d. Social
skill
39. Examples of social skills include all of the
following except:
a. Holding
conversations
b. Establishing
and maintaining friendships
c. Dating
d. Deviance
40. Grooming
is an example of……..
a. Assertive
skills
b. Behavioural
modification skills
c. Social
skills
d. Counselling
skills
41. Numerous
activities and skills that are a part of leading a happy and successful life
are collectively known as…..
a. Behavioural
modification skills
b. Social
skills
c. Counselling
skills
d. Stress
management skills
42. Different
ways of changing abnormal behavior include:
a. Classical
conditioning
b. Operant
conditioning
c. Modelling
d. All
of the above
43. The several types of admissions
in psychiatry include all of the following except:
a.
Voluntary
b.
Emergency
c.
Involuntary
d.
Elective
44. Discharge
planning involves working through phases, and in the ………..the admitting nurse
and multi-disciplinary team hold a meeting with the client and relatives in which they together begin to plan for the patient’s eventual discharge upon
recovery.
a. Working
phase
b. Termination
phase
c. Introduction
phase
d. Termination
phase
45. During
the …………….. the community mental health team may be called upon to make a home
visit to assess the home environment before a patient goes there.
a. Norming
phase
b. Working
phase
c. Termination
phase
d. Introduction
phase
46. The
……… is a transition phase in which the patient passes from a mental hospital to
the community and in which the patient is discharged.
a.
Working phase
b. Termination
phase
c. Introduction
phase
d. Norming phase
47. Brian a psychiatric patient was heard
formulating a sentence as follows “Braid, raid and aid.” Which disordered
speech pattern is this?
a. Word
salad
b. Neologism
c. Clang
association
d. Echolalia
48. Mary from a female ward was fond of coining
the phrase “Bing boom, big bang, a ragged rascal who bought a bang gang round
the rocks.” Which disordered speech pattern is this?
a. Word
salads
b. Neologism
c. Clang
association
d. Echolalia
49. Actions that result from ideas that come into
one’s mind frequently are known as………….
a. Obsessive
rituals
b. Compulsions
c. Waxy
flexibility
d. Habits
50. …………
is the interaction between people and their environment based on stimuli and
responses.
a. Counselling
b. Socialization
c. Communication
d. association
1. c)
How the person feels, acts, and perceives things
2. d)
Healing
3. c)
Application of psychiatric principles in nursing care
4. a)
Schizophrenia
5. c)
1964
6. c)
1968
7. a)
Thought broadcasting
8. b)
Paranoid schizophrenia
9. a)
Affective disorder
10. b)
Emotional stability
11. d)
Severe anxiety
12. a)
Women
13. a)
Anxiety disorder
14. c)
Post-traumatic disorder
15. b)
Phobia
16. b)
Social phobia
17. a)
Social phobia
18. d)
Good memory
19. c)
Counselling
20. a)
Psychotherapy
21. c)
Soler
22. c)
Agnosia
23. d)
Alzheimer’s disease
24. c)
Schizoaffective disorder
25. b)
Subjective perceived threat
26. d)
Valium
27. b)
Having disjointed ideas
28. b)
Chainama west
29. b)
Imipramine
30. b)
Trifluoperazine
31. b)
Inspecting oneself inwardly
32. c)
Mania
33. c) A
belief that one's thoughts are being shared by others
34. b)
Relational aggression
35. c)
Obsessional rumination
36. a)
Purposeless imitation of others
37. d)
Affect
38. d)
Social skill
39. d)
Deviance
40. c)
Social skills
41. b)
Social skills
42. d)
All of the above
43. d)
Elective
44. b)
Termination phase
45. b)
Working phase
46. b)
Termination phase
47. c)
Clang association
48. a)
Word salads
49. b)
Compulsions
50. b)
Socialization
SECTION
B: MATCHING ITEMS
(20 MARKS)
ALL
RESPONSES IN COLUMN II SHOULD BE USED ONCE
MATCH THE FOLLOWING DISORDERS OF
THINKING IN COLUMN I WITH THEIR DEFINITIONS IN COLUMN II
COLUMN I COLUMN II
51. …Delusions: A. Too much ideas flowing together.
52. …Retardation
of thought: B. No thinking in place.
53. …Fragmented
thinking: C. Beating about the bush.
54. ….Circumstantial
thinking: D. disjointed ideas.
55. ….Flight
of ideas: E. False belief
F. Ideas
coming into your mind frequently
MATCH THE FOLLOWING DISORDERS OF SPEECH
IN COLUMN I WITH THEIR CORRESPONDING DEFINITION IN COLUMN II
COLUMN I COLUMN
II
56. ....Mutism: G. Senseless speech.
57. ….Echolalia: H. Repeating what the
interviewer says.
58. ….Neologism: I. Formation of own words.
59. ...Word salads: J. Mixing of words that only make sense to the owner.
60. ...incoherent
speech:
K. When someone can’t talk
L.
Mokomo
MATCH
THE FOLLOWING TERMS USED IN PSYCHIATRY IN COLUMN I WITH THEIR CORRESPONDING
MEANING IN COLUMN II
COLUMN
I COLUMN II
61.
Disorientation…… A. opying what someone else is doing.
62.
Compulsion..… B. Doing opposite of
what you are taught.
63.
Negativism…. C. An act due to a repeated ideas coming
into your mind.
64.
Stereotyped activity... D.
maintaining of awkward posture.
65.
Waxy flexibility…. E.
Inability to recognize place, time, date, year/person.
MATCH
THE FOLLOWING DISORDERS OF MOOD IN COLUMN I OR AFFECT WITH THEIR CORRESPONDING
DEFINITIONS IN COLUMN II
COLUMN I COLUMN II
66. Ambivalence…. F. Excessive happiness.
67. Depression:.... G. Reduced affects.
68. Flat
affects…. H. Unexpected behavior or affect.
69. Incongruent
affect…. I.
Un-aroused affect
70. Euphoria……. J. Two conflicting ideas at the same time.
MATCHING
ITEMS
Disorders
of Thinking: 51. E. Delusions: False belief
52. B.
Retardation of thought: No thinking in place
53. D.
Fragmented thinking: Disjointed ideas
54. C.
Circumstantial thinking: Beating about the bush
55. A.
Flight of ideas: Too many ideas flowing together
Disorders
of Speech: 56. K. Mutism: When someone can’t talk
57. H.
Echolalia: Repeating what the interviewer says
58. I.
Neologism: Formation of own words
59. J.
Word salads: Mixing of words that only make sense to the owner
60. G.
Incoherent speech: Senseless speech
Terms
Used in Psychiatry: 61. E. Disorientation: Inability to recognize place, time,
date, year/person
62. C.
Compulsion: An act due to repeated ideas coming into your mind
63. B.
Negativism: Doing opposite of what you are taught
64. A.
Stereotyped activity: Copying what someone else is doing
65. D.
Waxy flexibility: Maintaining awkward posture
Disorders
of Mood or Affect: 66. J. Ambivalence: Two conflicting ideas at the same time
67. G.
Depression: Reduced affects
68. I.
Flat affects: Un-aroused affect
69. H.
Incongruent affect: Unexpected behavior or affect
70. F.
Euphoria: Excessive happiness
SECTION
C; COMPLETION QUESTIONS
FILL
IN THE BLANKS WITH ONE OR TWO WORDS
71. Voluntary
admission is the entry of a patient into a psychiatric hospital with his or
her……………………….
72. ………admission
is an unexpected and sudden entry of a patient into hospital due to a sudden
health crisis.
73. ….
is the entry and detention of a patient within an institution without his
consent.
74. Discharge
planning involves working through phases, and in the ………..phase the admitting nurse and multi-disciplinary
team hold a meeting with the client and relatives in which they together begin to plan for the patient’s eventual discharge upon
recovery.
75. The
………phase is when the patient goes into the community, it is a transition phase
in which the patient passes from mental hospital to the community and in which
the patient is discharged.
76. During
the ……………..phase the community mental health team may be called upon to make a
home visit to assess the home environment before a patient goes there.
77. The
classic feature of delirium is …………………………………of consciousness
78. ………………………..is
a perception experienced in the absence of an external stimulus
79. Catatonic
schizophrenia is characterized by disorders of………
80. Examples
of neuroses include; Anxiety Neurosis, Obsessive Compulsive Neurosis and …………..
81. Depression
is categorized as ……or reactive
82. Decreased
sexual activity could be a manifestation of ……………….depression
83. When
nursing a patient with suicidal behavior ensure that the………….. is safe for the
patient
84. Anxiety
and panic disorder can be worsened by intake of……………and drugs
85. Symptoms
such as heart palpitations, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnoea are characteristic of
…………………………………………...
86. …………..….. is
psychiatric nursing skill which implies watching carefully the way something
happens or the way someone does something
87. The…………………………………………is
designed to obtain information about the specific aspect of an individual’s
mental experiences and behavior at the time of interview .
88. The …………….. skill is about
Inspecting oneself inwardly.
89. ………….…… are a psychiatric clinical feature
in which the patient has to do things in a particular order, or a certain
number of times.
90. The
internal debates in which arguments for and against even the simplest everyday
actions are reviewed endlessly are called……….
91. ………….….teach patient step by step way of changing
bad behavior and learn good manners.
92. ………………… skills are used to help patients change abnormal behaviour
93. …………..Train patients to express themselves in an appropriate way
94. …… ….. help a client solve
a problem successfully
95. ……….…………is about the reciprocal exchange of information, ideas and
feelings
96. Acting to bring about a desired treatment outcome is known as…therapeutic
skills….
97. Actions
nurses take to help, treat or deliver nursing care to clients so that they may
recover or get well are known as……………….
98. The
leaving of the hospital by a patient which involves a corresponding discharge
note is called……………..
99. An examination that is conducted the first
time a patient comes to the health facility with a complaint and may also be
conducted upon admission is called………….…
100. ……….……..
is a process by which complex trends are organized into groups, classes or
ranks, in order to put together things that must be similar to each other and
to isolate those that are different.
71. Voluntary
admission is the entry of a patient into a psychiatric hospital with his or her
consent.
72. Emergency
admission is an unexpected and sudden entry of a patient into hospital due to a
sudden health crisis.
73. Involuntary is
the entry and detention of a patient within an institution without his consent.
74. Discharge
planning involves working through phases, and in the introduction phase
the admitting nurse and multi-disciplinary team hold a meeting with the client
and relatives in which they together begin to plan for the patient’s eventual
discharge upon recovery.
75. The termination
phase is when the patient goes into the community, it is a transition phase in
which the patient passes from mental hospital to the community and in which the
patient is discharged.
76. During
the norming phase the community mental health team may be called upon to
make a home visit to assess the home environment before a patient goes there.
77. The
classic feature of delirium is clouding of consciousness.
78. Hallucination is
a perception experienced in the absence of an external stimulus.
79. Catatonic
schizophrenia is characterized by disorders of movement.
80. Examples
of neuroses include; Anxiety Neurosis, Obsessive Compulsive Neurosis and Hysterical
Neurosis.
81. Depression
is categorized as endogenous or reactive.
82. Decreased
sexual activity could be a manifestation of endogenous depression.
83. When
nursing a patient with suicidal behavior ensure that the environment is
safe for the patient.
84. Anxiety
and panic disorder can be worsened by intake of caffeine and drugs.
85. Symptoms
such as heart palpitations, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea are characteristic of panic
attacks.
86. Observation is
a psychiatric nursing skill which implies watching carefully the way something
happens or the way someone does something.
87. The mental
state examination is designed to obtain information about the specific
aspect of an individual’s mental experiences and behavior at the time of
interview.
88. The self-awareness
skill is about Inspecting oneself inwardly.
89. Compulsions are
a psychiatric clinical feature in which the patient has to do things in a
particular order, or a certain number of times.
90. The
internal debates in which arguments for and against even the simplest everyday
actions are reviewed endlessly are called obsessional doubts.
91. Counselling
skills teach patients step by step way of changing bad behavior and learn good
manners.
92. Behavioural
modification skills are used to help patients change
abnormal behavior.
93. Communication
skills train patients to express themselves in an appropriate way.
94. Problem-solving
skills help a client solve a problem successfully.
95. Communication is
about the reciprocal exchange of information, ideas and feelings.
96. Acting
to bring about a desired treatment outcome is known as therapeutic skills.
97. Actions
nurses take to help, treat or deliver nursing care to clients so that they may
recover or get well are known as therapeutic interventions.
98. The
leaving of the hospital by a patient which involves a corresponding discharge
note is called discharge.
99. An
examination that is conducted the first time a patient comes to the health
facility with a complaint and may also be conducted upon admission is called initial
assessment.
100.
Classification is
a process by which complex trends are organized into groups, classes or ranks,
in order to put together things that must be similar to each other and to
isolate those that are different.
ANSWER TWO QUESTIONS ONLY.
EACH QUESTION CARRIES (100 MARKS).
COMPULSORY QUESTION
Mr Mbuzi
phiri male aged 36 years married with 4 children is admitted to Chainama Hills Hospital with history of alcohol abuse.
The wife said her husband sometimes experiences tremor. He has been suspended
at work for absenteeism. The wife explains that he has impaired thinking and
hallucinations as well. On examination a provisional diagnosis of alcoholism
was made.
A) State six (6) social effects of
alcohol abuse 20%
B) Discuss how alcohol abuse can be
prevented 30%
C) Describe in details the management of
Mr. Mbuzi 50%
A) State six (6) social effects of alcohol abuse:
- Family
Dysfunction: Alcohol abuse can strain relationships
within the family, leading to conflicts, breakdowns in communication, and
domestic violence.
- Financial
Problems: Excessive spending on alcohol can lead to
financial instability, affecting the ability to meet household expenses
and save for the future.
- Social
Isolation: Alcohol abuse may lead to withdrawal from
social activities and friendships, as individuals prioritize drinking over
social interactions.
- Legal
Issues: Alcohol-related behaviors such as drunk
driving or disorderly conduct can result in legal consequences, including
fines, license suspension, or even imprisonment.
- Employment
Issues: Absenteeism, decreased productivity, and
job loss can occur due to alcohol abuse, leading to financial strain and
unemployment.
- Stigmatization:
Society often stigmatizes individuals struggling with alcohol abuse,
leading to feelings of shame, guilt, and isolation, which can further
exacerbate the problem.
B) Discuss how alcohol abuse can be prevented:
- Education
and Awareness: Promoting awareness about the risks and
consequences of alcohol abuse through public health campaigns, school
programs, and community events can help prevent alcohol abuse.
- Early
Intervention: Identifying and addressing risk factors
for alcohol abuse early, such as childhood trauma, peer pressure, or
mental health issues, can prevent the development of problematic drinking
behaviors.
- Regulation
and Legislation: Implementing policies and regulations,
such as minimum legal drinking ages, restricted alcohol advertising, and
taxation on alcohol products, can help reduce alcohol consumption and
prevent abuse.
- Access
to Support Services: Providing accessible and affordable
support services, including counseling, therapy, and addiction treatment
programs, can help individuals struggling with alcohol abuse seek help and
overcome their addiction.
- Community
Support: Building supportive communities that
offer alternatives to alcohol-centric socializing, such as sports clubs,
hobby groups, and cultural events, can provide individuals with healthy
outlets and social connections.
- Family
Involvement: Educating families about the warning
signs of alcohol abuse and encouraging open communication can help create
a supportive environment for individuals at risk and facilitate early
intervention and treatment.
C) Describe in detail the management of Mr. Mbuzi:
- Assessment:
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of Mr. Mbuzi's physical health, mental
health, social support system, and alcohol use history to develop an
individualized treatment plan.
- Detoxification:
Provide medical supervision and support during the detoxification process
to manage withdrawal symptoms safely and effectively, ensuring Mr. Mbuzi's
physical stability.
- Psychosocial
Interventions: Offer counseling, therapy, and support
groups to address the underlying factors contributing to Mr. Mbuzi's
alcohol abuse, such as stress, trauma, or co-occurring mental health
disorders.
- Medication-Assisted
Treatment (MAT): Consider pharmacological interventions,
such as medications to reduce cravings or manage co-occurring mental
health symptoms, as part of Mr. Mbuzi's treatment plan.
- Relapse
Prevention: Develop coping strategies, stress
management techniques, and relapse prevention skills to empower Mr. Mbuzi
to maintain sobriety and manage triggers and cravings effectively.
- Family
Therapy: Involve Mr. Mbuzi's family in the
treatment process, offering education, counseling, and support to help
rebuild relationships, improve communication, and address enabling
behaviors.
- Aftercare
Planning: Develop a comprehensive aftercare plan
that includes ongoing support, follow-up appointments, and referrals to
community resources to ensure continuity of care and long-term recovery
success for Mr. Mbuzi.
1.
Mr.
Mutokofita aged 30 years is brought to Chainama Hospital Ward X with history of
wondering about and self -neglect for the past 3 months. On admission, the
Doctor conduct a Mental State Examination and a diagnosis of Dementia is made
a)
Define Dementia
5 marks
b)
Explain
five (5) causes/predisposing factors of Dementia 25 marks
c)
State
five (5) cardinal signs of Dementia
20 marks
d)
Discuss
how you are going to nurse Mr. Mutokofita during his stay in hospital
50
marks
a) Define Dementia: Dementia is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by a decline in cognitive function, including memory loss, reasoning, judgment, and language skills, to the extent that it interferes with daily functioning. It is not a specific disease but rather a syndrome caused by various underlying conditions that affect the brain's ability to process information and communicate effectively.
b) Explain five (5) causes/predisposing factors of Dementia:
- Alzheimer's Disease: The most common cause of dementia, Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, leading to the death of brain cells and progressive cognitive decline.
- Vascular Dementia: Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often due to conditions such as stroke, small vessel disease, or hypertension, vascular dementia results in cognitive impairment related to damage to brain tissue.
- Lewy Body Dementia: This type of dementia is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, leading to symptoms such as visual hallucinations, fluctuating cognition, and motor impairments resembling Parkinson's disease.
- Frontotemporal Dementia: This form of dementia is characterized by the degeneration of nerve cells in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, resulting in changes in behavior, personality, and language abilities.
- Mixed Dementia: Some individuals may have a combination of different types of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia, which can result in a more complex clinical presentation and progression of symptoms.
c) State five (5) cardinal signs of Dementia:
- Memory Loss: Persistent forgetfulness, particularly of recent events or information, is a hallmark symptom of dementia.
- Impaired Judgment and Reasoning: Individuals with dementia may have difficulty making decisions, solving problems, and understanding cause-and-effect relationships.
- Language and Communication Difficulties: Dementia can affect a person's ability to express themselves verbally, understand spoken or written language, and participate in conversations.
- Impaired Visual Perception: Some individuals with dementia may experience difficulties with visual perception, leading to problems with depth perception, object recognition, and spatial awareness.
- Changes in Mood and Behavior: Dementia can cause mood swings, irritability, agitation, apathy, and social withdrawal, which can vary depending on the type and stage of the condition.
d) Discuss how you are going to nurse Mr. Mutokofita during his stay in hospital:
- Comprehensive Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of Mr. Mutokofita's physical health, mental status, cognitive function, and psychosocial needs to develop an individualized care plan.
- Person-Centered Care: Provide care that is tailored to Mr. Mutokofita's preferences, abilities, and limitations, respecting his dignity, autonomy, and rights throughout his hospitalization.
- Safety Measures: Implement safety precautions to prevent falls, wandering, and self-harm, including environmental modifications, close supervision, and the use of assistive devices.
- Medication Management: Administer prescribed medications as ordered, monitor for side effects and therapeutic response, and collaborate with the healthcare team to optimize pharmacological treatment.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engage Mr. Mutokofita in activities that promote cognitive stimulation, such as reminiscence therapy, puzzles, games, and social interactions, to help maintain cognitive function and improve quality of life.
- Emotional Support: Offer emotional support and reassurance to Mr. Mutokofita and his family members, addressing feelings of confusion, frustration, and distress associated with dementia.
- Nutritional Support: Ensure that Mr. Mutokofita receives adequate nutrition and hydration, monitoring his dietary intake, offering assistance with feeding if necessary, and addressing any swallowing difficulties.
- Continuity of Care: Collaborate with interdisciplinary team members, including physicians, nurses, therapists, and social workers, to coordinate care, address complex needs, and facilitate transitions of care during Mr. Mutokofita's hospitalization and discharge planning.




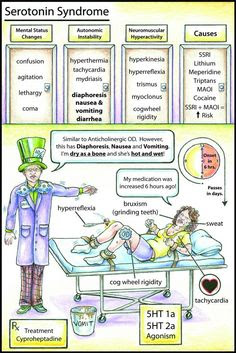




.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment