CHANGE MANAGEMENT
CHANGE MANAGEMENT
Three types of change commonly encountered in organizations are:
Organizational Change: This involves changes in the structure, processes, culture, or strategies of an organization. It could include mergers, acquisitions, reorganizations, or changes in leadership.
Technological Change: This refers to the adoption or implementation of new technologies within an organization. This could involve upgrading existing systems, implementing new software, or integrating automation into processes.
Individual Change: This type of change focuses on changes in behaviors, attitudes, or skills of individual employees within an organization. It could involve training programs, coaching, or performance management initiatives.
Managing planned change typically involves several steps:
Assessment and Planning:
- Identify the need for change: This involves analyzing the current state of the organization, understanding the reasons for change, and determining the desired future state.
- Set objectives and goals: Clearly define what the organization aims to achieve through the change process. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a change management plan: This plan should outline the strategies, resources, timeline, and communication channels needed to implement the change effectively. It should also identify potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Implementation:
- Communicate the change: Effective communication is crucial to gain buy-in and support from employees. Leaders should clearly communicate the reasons for change, the expected outcomes, and how it will impact individuals within the organization.
- Provide support and resources: Ensure that employees have the necessary tools, training, and support to adapt to the change. This could involve providing training programs, offering mentoring or coaching, and addressing any concerns or resistance.
- Monitor progress: Regularly assess the progress of the change initiative against the established objectives and goals. This allows for adjustments to be made if necessary and helps to keep the change process on track.
Evaluation and Reinforcement:
- Evaluate the results: Assess the outcomes of the change initiative to determine its effectiveness in achieving the desired objectives. This could involve collecting feedback from employees, analyzing performance metrics, and comparing the actual results with the expected outcomes.
- Reinforce the change: Recognize and reward employees who have embraced the change and contributed to its success. Reinforcement can help to embed the change into the organizational culture and ensure its sustainability in the long term.
- Learn and adapt: Reflect on the lessons learned from the change process and use this knowledge to inform future change initiatives. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for organizations to remain agile and responsive to evolving needs and challenges.
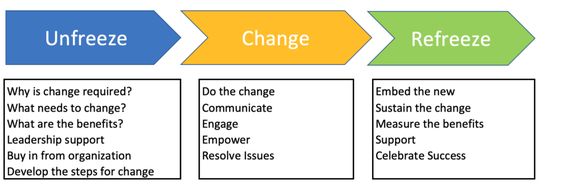
Kurt Lewin, a psychologist, is often credited with developing the foundational theories of change management. His model is often referred to as the "Unfreeze-Change-Refreeze" model, although he did not use these exact terms himself. The model emphasizes the idea that change involves a process of unfreezing the current state, making the change, and then refreezing the new state to make it stable. Here's a breakdown of Lewin's change management theory:
Unfreezing:
- In this stage, the organization prepares for change by creating the motivation to change. This involves breaking down the existing mindset, beliefs, and behaviors that are resistant to change.
- Unfreezing can be achieved through various means, such as creating awareness of the need for change, communicating the reasons behind the change, and providing a sense of urgency.
- It may also involve addressing any fears, anxieties, or resistance to change among employees by fostering an environment of trust and openness.
Change:
- Once the organization is unfrozen, it can move into the change stage, where the actual changes are implemented. This involves introducing new processes, structures, systems, or behaviors to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Change may be gradual or abrupt, depending on the nature of the change and the organization's readiness to adapt.
- Effective communication, leadership support, and employee involvement are essential during this stage to ensure a smooth transition and minimize resistance.
Refreezing:
- In the final stage, the organization stabilizes the change by reinforcing the new behaviors, processes, or structures. This involves embedding the change into the organizational culture and making it the new norm.
- Refreezing helps to ensure that the change becomes sustainable over the long term and prevents the organization from reverting to its old ways.
- Strategies for refreezing may include providing training and support, aligning incentives and rewards with the desired behaviors, and continuously reinforcing the importance of the change.
Lewin's model emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological and social aspects of change, such as resistance to change and the need for support and motivation. It provides a structured framework for managing change effectively by addressing these factors throughout the change process.
Kurt Lewin’s Change Management Theory talks about how planned change process should be introduced in an organization. He believed that planned change should begin with an analysis and diagnosis of the current situation.
TASK – Mention 3 types of change. Explain three steps that are involved in managing a planned change.
MARKING KEY-CHANGE MANAGEMENT
Types of change
• Planned Change1 Mark
• Unplanned Change1 Mark
• Transformation Change1 Mark
STEPS
Unfreezing-This means abandoning old practices before adopting new ones. He believed that if individuals have to change, their current behavior patterns must be unfrozen as away of reducing resistance to change. Explain why change is necessary.(3 Marks)
Transition -This is movement from current to planned position. Management of this process involves winning the support of all the affected people and getting them to participate.
(2 Marks)
Refreeze- Sustainability of the change and making it a model of practice. Important way of sustaining change is by use of rewards to those that continue in the new behavior. (2 Marks)




.jpg)

.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment