IMMUNITY
IMMUNITY
The immune system is a system of
biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against
disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of
agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the
organism's own healthy tissue.
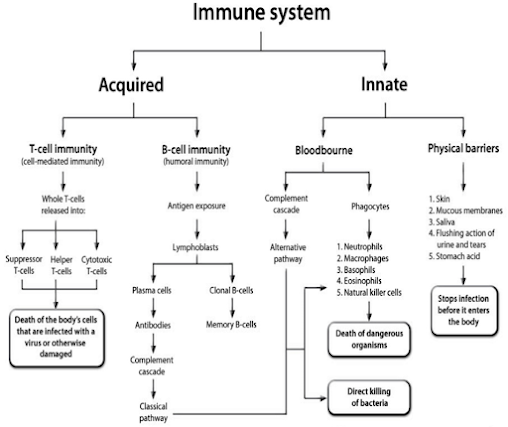
TYPES OF IMMUNITY
Immunity is divided into two divisions
- Non – specific (innate immune system/inherent)
- Specific/adaptive immunity which gives acquired immunity.
NON SPECIFIC/NATIVE/INNATE
A portion of immunity resulting from general processes
rather than processes directed at specific diseases or organisms.
This include resistance of skin to invasion by
organisms, destruction by acid secretion by stomach and digestive enzymes
organisms swallowed, phagocytosis of bacteria and other invader by leukocytes
and cells of the tissue macrophage system.
SPECIFIC
OR ADAPTIVE OR ACQUIRED
Acquired immunity is the type of immunity which has
specificity against foreign substances.
Much of our immunity is caused by this system.This is acquired by
previous experience of the organisms or its products.
TYPES OF AQUIRED IMMUNITY
1. NATURAL
ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
This is passed
from one generation to another though gene oar if one has suffered from a disease.
It may be passive or active
Active: antibodies are produced by the immune person.
Passive: antibodies are produced elsewhere and are
then given to the person.
A. NATURAL PASSIVE ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
Here the antibody is obtained by the young
from the mother either across the placenta or in breast milk. The human
placenta allows maternal antibody to pass into the foetal circulation. The baby is then born having maternal
antibodies against the diseases to which the mother is immune. This provides
the baby with defence immediately after birth.
The antibodies do not persist. They disappear after a few months. Humans
also obtain antibody in the breast milk. This is absorbed from the intestine
and enters the circulation.
B. NUTURAL ACTIVE ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
Natural active acquired immunity: this is
the type of immunity which is acquired in response to the entry of a live
pathogen into the body (i.e., in response to an actual infection) - it has long duration this applies to typhoid
fever, measles and small pox.
2. ARTIFICIAL ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
This is also subdivided into active or
passive according to whether the person actively participates by making his own
antibodies (active) or only passively receives antibodies present in
therapeutic sera.
A. ARTIFICIAL PASSIVE ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
In here the antibody is obtained or
protection is derived from the infection (serum) of prepared or readymade
antibodies. E.g. diphtheria, tetanus or gas gangrene. (Antitoxic sera protection is received
immediately but does not last long because infected serum with its antibodies
fairly rapidly.
B. ARTIFICIAL ACTIVE AQUIRED IMMUNITY
This type of immunity develops as a result
of vaccination with dead or attenuated pathogens or its toxins. The body is
then able to produce its own antibodies against the pathogen.



.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment